Improved graft survival by using three-dimensional printing of intra-abdominal cavity to prevent large-for-size syndrome in liv
Backgrounds/Aims: While large-for-size syndrome is uncommon in liver transplantation (LT), it can result in fatal outcome. To prevent such fatality, we manufactured 3D-printed intra-abdominal cavity replicas to provide intuitive understanding of the sizes of the graft and the patient’s abdomen in patients with small body size between July 2020 and February 2022. Methods: Clinical outcomes were compared between patients using our 3D model during LT, and patients who underwent LT without 3D model by using 1 : 5 ratio propensity score-matched analysis. Results: After matching, a total of 20 patients using 3D-printed abdominal cavity model and 100 patients of the control group were included in this study. There were no significant differences in 30-day postoperative complication (50.0% vs. 64.0%, p = 0.356) and the incidence of large-for-size syndrome (0% vs. 7%, p = 0.599). Overall survival of the 3D-printed group was similar to that of the control group (p = 0.665), but graft survival was significantly superior in the 3D-printed group, compared to the control group (p = 0.034). Conclusions: Since it showed better graft survival, as well as low cost and short production time, our 3D-printing protocol can be a feasible option for patients with small abdominal cavity to prevent large-for-size syndrome after LT. This study explores the use of 3D-printed abdominal cavity models in liver transplantation (LT) to address large-for-size syndrome, which can lead to fatal outcomes. A total of 20 patients underwent LT using 3D-printed models, and their outcomes were compared with a control group of 100 patients via propensity score matching. Key Findings: - Graft Survival: The 3D-printed group had significantly superior graft survival compared to the control group. - Cost and Time Efficiency: Manufacturing cost was approximately $1.25 per model, with a production time of about 6-7 hours, showcasing cost-effectiveness and practicality. - Applications: The models were particularly helpful for recipients with small abdominal cavities, aiding in selecting appropriate grafts and preventing complications. Conclusion: The integration of 3D-printed models into clinical practice improves surgical planning and outcomes while being cost-effective and efficient. 3D printing technology is redefining surgical approaches, providing personalized anatomical models for preoperative planning and intraoperative guidance. Its application in liver transplantation exemplifies its potential to improve graft selection, prevent complications, and enhance surgical outcomes. With advancements in cost and production time, 3D printing is becoming an accessible tool for precision medicine. 이 연구는 간 이식(LT) 중 과대 크기 증후군을 예방하기 위해 3D 프린팅 복강 모델을 활용한 사례를 다룹니다. 3D 프린팅 모델을 이용하여 간 이식을 받은 20명의 환자와 100명의 대조군 환자 결과를 성향 점수 매칭을 통해 비교했습니다. 주요 결과: - 이식 생존율: 3D 프린팅 모델을 사용한 그룹이 대조군에 비해 이식 생존율이 유의미하게 높았습니다. - 비용 및 시간 효율성: 모델 제작 비용은 약 $1.25, 제작 시간은 약 6~7시간으로 비용 효율성과 실용성을 보여주었습니다. - 적용 사례: 특히 작은 복강을 가진 수혜자들에게 적합한 간을 선택하고 합병증을 예방하는 데 유용했습니다. - 결론: 3D 프린팅 모델의 임상 적용은 수술 계획과 결과를 개선하며 비용 효율적이고 실용적인 방법임을 입증했습니다. 3D 프린팅 기술은 수술 접근 방식을 혁신하며, 수술 전 계획 및 수술 중 가이드를 위한 개인 맞춤형 해부학적 모델을 제공합니다. 간 이식 분야에서의 활용은 이식 간 선택을 개선하고 합병증을 예방하며 수술 결과를 향상시키는 잠재력을 보여줍니다. 비용 및 제작 시간의 발전으로 3D 프린팅은 정밀 의학의 도구로 점점 더 접근 가능해지고 있습니다.
Author jsrrules
Date 2024.12.08
3D Printing Model of Abdominal Cavity of Liver Transplantation Recipient to Prevent Large-for-Size Syndrome
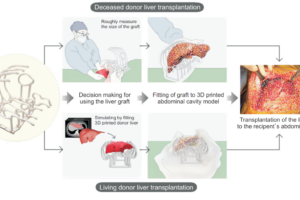
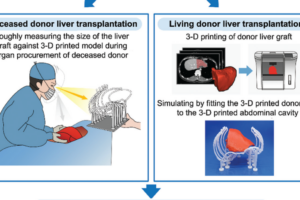
Abstract: The application of three-dimensional (3D) printing has been increasing and we invented cost-effective and time-saving 3D printed model of intra-abdominal cavity which was utilized in liver transplantation (LT) to prevent large-for-size syndrome. 3D printings were performed on potential adult recipients with small cavity and pediatric patients scheduled for transplantation during July 2020 – September 2021. Based on the computed tomography of the recipient, the inner surface of the abdominal cavity was outlined. The line was marked with a distance of 1 – 3 cm. Then, the outlined data were reconstructed as a 3D model and printed by a fused deposition modeling type 3D printer with a thickness of 2 mm. Pillars and footings for holding the lines were printed and assembled altogether. During deceased donor organ procurement, the size of the graft was compared to that of the printed model. For living donor LT, preoperatively planned liver graft was printed and was physically placed into the 3D printed abdominal cavity. All the 16 cases with 3D printed abdominal cavity showed appropriate fitting of the donor’s liver graft to both the 3D printed model and actual recipient’s abdominal cavity with no large-for-size syndrome after LT. Median time for manufacturing the model was 576 min (IQR 434 – 680) and estimated median cost for the filament was US$ 1.6 (IQR 1.2 – 1.7). The 3D printed abdominal cavity model can be manufactured in <10 h and was useful for preventing large-for-size syndrome in small-sized recipients. Int J Bioprint. 8(4):609. http://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v8i4.609 This study demonstrates the use of a cost-effective and time-efficient 3D-printed abdominal cavity model in liver transplantation (LT) to prevent large-for-size syndrome. By using computed tomography data, 16 patients (10 adults and 6 pediatric recipients) underwent LT with the aid of 3D models. The printed models provided a realistic reference for evaluating graft fit into the recipient's abdominal cavity, enabling precise surgical planning and decision-making. Key findings: - Manufacturing time: <10 hours per model. - Median cost: $1.6 per model. - No cases of large-for-size syndrome reported. Benefits: - Low cost and quick production. - Improved preoperative planning. - Better graft fitting evaluation for small recipients or complex cases. 3D printing is revolutionizing surgery by offering patient-specific models for preoperative planning, intraoperative guidance, and personalized care. It is especially impactful in liver transplantation and other complex surgeries by enhancing precision, improving surgical outcomes, and reducing risks associated with anatomical constraints or unexpected complications. 이 연구는 간 이식(LT) 중 과대 크기 증후군(large-for-size syndrome)을 예방하기 위해 비용 효율적이고 시간 절약적인 3D 프린팅 복강 모델을 활용한 사례를 보여줍니다. 컴퓨터 단층 촬영 데이터를 기반으로 16명의 환자(성인 10명, 소아 6명)가 3D 모델을 이용해 간 이식을 받았으며, 출력된 모델은 수혜자의 복강에 이식 간의 적합성을 평가하는 현실적인 참조 자료를 제공하여 정확한 수술 계획과 결정을 가능하게 했습니다. 주요 발견: - 제작 시간: 모델당 10시간 미만. - 중간 비용: 모델당 약 1.6달러. - 과대 크기 증후군 발생 사례 없음. 장점: - 저렴한 비용과 빠른 제작. - 수술 전 계획 개선. - 소형 수혜자 또는 복잡한 사례에서 이식 간의 적합성 평가 용이. 3D 프린팅은 수술 전 계획, 수술 중 가이드, 맞춤형 치료를 위한 환자 맞춤형 모델을 제공함으로써 외과 수술을 혁신하고 있습니다. 특히 간 이식 및 복잡한 수술에서 정확도를 높이고 수술 결과를 개선하며 해부학적 제약이나 예기치 않은 합병증과 관련된 위험을 줄이는 데 큰 영향을 미칩니다.
Author jsrrules
Date 2024.12.08
[Case Report] Application of three-dimensional printing for intraoperative guidance during liver resection of a hepatocellula
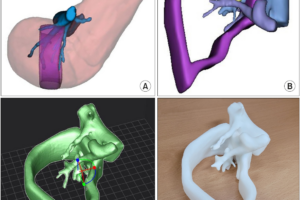
Abstract While 3D printing is adapted usefully in certain field of surgery, its application in liver surgery was limited. Here, we introduce our experience for using 3D printing for intraoperative guidance during liver resection in a case for HCC with an intrahepatic metastasis at a sophisticated location. A 50 years old male patient was diagnosed 4.7 cm-sized hepatocellular carcinoma located on segment 3 with and an intrahepatic metastasis located on segment 8 which was between right anterior portal vein, middle hepatic vein and right hepatic vein. Since radiofrequency ablation appeared to be inappropriate, surgical resection was planned. However, the patient had a cirrhotic liver and left liver was estimated to be 47% according to volume measurement. Therefore, we planned a two-step procedure by performing left hemihepatectomy preserving the middle hepatic vein and additionally removing the intrahepatic metastasis by tumorectomy. For better guidance, we made a 3D printed model tailored for using it as a guidance during operation, and the accuracy of 3D-printed model helped the surgical team perform a safe operation. The patient underwent adjuvant proton beam therapy on the site of tumorectomy and did not experience recurrence. (Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2021;25:265-269) Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2021;25:265-269 https://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.265 This case report outlines the application of 3D printing technology to aid in liver resection surgery for a 50-year-old patient with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and an intrahepatic metastasis located in a challenging position. The patient's condition involved a cirrhotic liver and complex vascular anatomy, necessitating precise surgical planning. Key points include: Use of 3D Printing: A 3D-printed model of the liver was created to guide the surgery, enabling better visualization of the tumor's location relative to critical vascular structures. Surgical Plan: The patient underwent a two-step surgery involving left hemihepatectomy with preservation of the middle hepatic vein and additional tumorectomy of the intrahepatic metastasis. Outcome: The model improved intraoperative precision, leading to successful tumor removal with clear margins. Post-surgery, the patient received adjuvant proton beam therapy and showed no recurrence during follow-up. Advantages: The 3D model provided a direct, practical guide during the operation, improving safety and efficiency. The cost and time for the model were relatively low. Meaning in the Industry of 3D Printing and Surgery 3D printing is transforming surgical planning and intraoperative guidance, particularly in complex and high-risk cases. Its applications include: Preoperative Planning: 3D-printed models allow surgeons to visualize and understand intricate anatomical relationships, enhancing surgical strategy. Intraoperative Guidance: Models serve as tangible references during procedures, aiding in precision and reducing risks. Education and Communication: They are valuable for training surgeons and explaining procedures to patients. Cost-Effectiveness: While traditionally perceived as expensive, advancements have made 3D printing more accessible, as demonstrated in the case report. Broad Potential: Beyond liver surgery, 3D printing is widely used in orthopedic, cardiovascular, and maxillofacial surgeries, among others. This case highlights the emerging role of 3D printing as a tool for enhancing surgical outcomes in complex procedures, representing a significant step forward in personalized medicine and patient-specific surgical approaches. 논문 요약 이 증례 보고는 50세 환자의 간세포암(HCC)과 복잡한 위치에 있는 간내 전이 치료를 위한 간 절제 수술에서 3D 프린팅 기술을 활용한 사례를 다루고 있습니다. 환자는 간경변과 복잡한 혈관 구조를 가지고 있어 정확한 수술 계획이 필요했습니다. 주요 내용: 3D 프린팅 활용: 간의 3D 프린팅 모델을 제작하여 종양과 주요 혈관 구조의 위치를 명확히 시각화하여 수술을 지원했습니다. 수술 계획: 중간 간정맥을 보존하면서 좌간 절제술을 시행하고, 간내 전이를 추가로 절제하는 2단계 수술을 진행했습니다. 결과: 3D 모델은 수술 중 정확도를 높여 종양을 성공적으로 제거하고 깨끗한 절제 경계를 확보하는 데 기여했습니다. 수술 후 환자는 부가적인 양성자 빔 치료를 받았으며, 추적 관찰 기간 동안 재발이 관찰되지 않았습니다. 장점: 3D 모델은 수술 중 실용적인 가이드를 제공하여 안전성과 효율성을 개선했으며, 제작 비용과 시간이 비교적 저렴했습니다. 3D 프린팅과 수술 산업에서의 의미 3D 프린팅은 복잡하고 고위험인 수술에서 수술 계획 및 수술 중 가이드를 제공하며, 의료 분야를 혁신적으로 변화시키고 있습니다. 그 의미는 다음과 같습니다: 수술 전 계획: 3D 프린팅 모델은 복잡한 해부학적 구조를 명확히 시각화하여 더 나은 수술 전략을 수립하도록 돕습니다. 수술 중 가이드: 모델은 수술 중 참고 자료로 활용되어 정밀도를 높이고 위험을 줄여줍니다. 교육 및 소통: 모델은 의사 교육 및 환자에게 수술 과정을 설명하는 데 유용합니다. 비용 효율성: 전통적으로 비용이 높다고 여겨졌지만, 기술 발전으로 접근성이 개선되었습니다. 본 논문에서도 낮은 비용과 시간을 입증했습니다. 광범위한 적용: 간 수술 외에도 3D 프린팅은 정형외과, 심혈관, 악안면 수술 등 다양한 분야에서 사용됩니다. 이 증례는 3D 프린팅이 복잡한 수술에서 수술 결과를 개선하는 도구로서 부각되고 있으며, 개인 맞춤형 의학 및 환자 중심 수술 접근법에서 중요한 진전을 보여줍니다.

