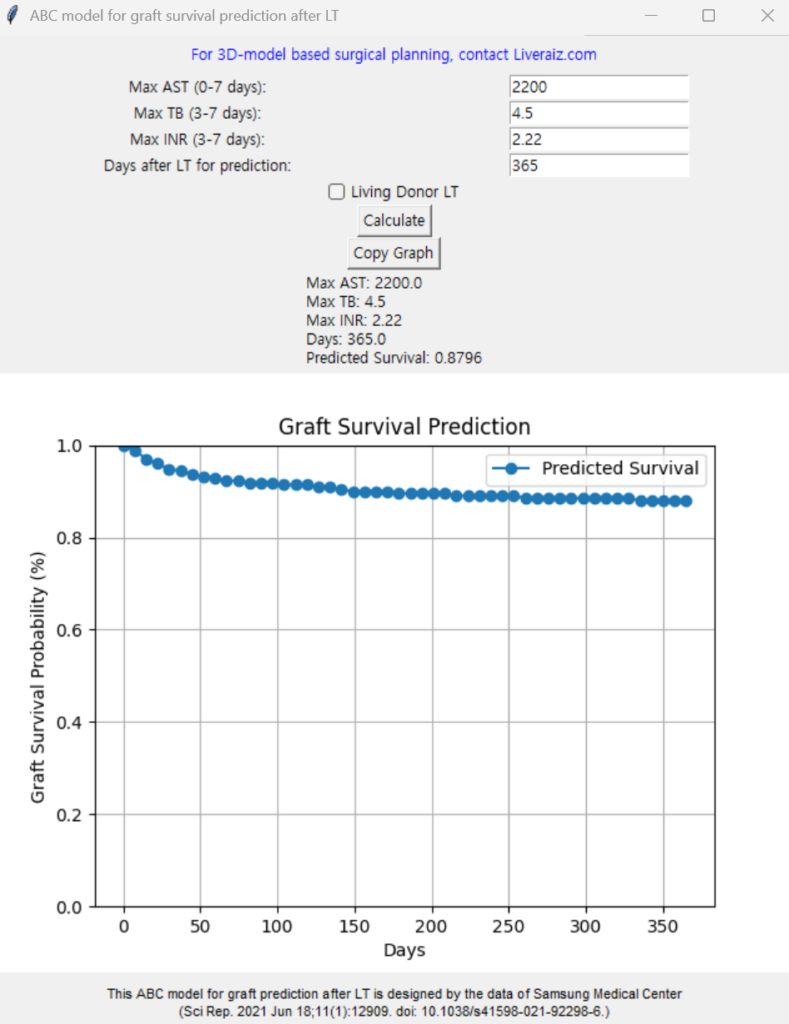
Prediction model for graft failure after liver transplantation-chatGPT coded program for Windows
Abstract This study was designed to build models predicting early graft failure after liver transplantation. Cox regression model for predicting early graft failure after liver transplantation using posttransplantation aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and international normalized ratio of prothrombin time was constructed based on data from both living donor (n = 1153) and deceased donor (n = 359) liver transplantation performed during 2004 to 2018. The model was compared with Model for Early Allograft Function Scoring (MEAF) and early allograft dysfunction (EAD) with their C-index and time-dependent area-under-curve (AUC). The C-index of the model for living donor (0.73, CI = 0.67–0.79) was significantly higher compared to those of both MEAF (0.69, P = 0.03) and EAD (0.66, P = 0.001) while C-index for deceased donor (0.74, CI = 0.65–0.83) was only significantly higher compared to C-index of EAD. (0.66, P = 0.002) Time-dependent AUC at 2 weeks of living donor (0.96, CI = 0.91–1.00) and deceased donor (0.98, CI = 0.96–1.00) were significantly higher compared to those of EAD. (both 0.83, P < 0.001 for living donor and deceased donor) Time-dependent AUC at 4 weeks of living donor (0.93, CI = 0.86–0.99) was significantly higher compared to those of both MEAF (0.87, P = 0.02) and EAD. (0.84, P = 0.02) Time-dependent AUC at 4 weeks of deceased donor (0.94, CI = 0.89– 1.00) was significantly higher compared to both MEAF (0.82, P = 0.02) and EAD. (0.81, P < 0.001). The prediction model for early graft failure after liver transplantation showed high predictability and validity with higher predictability compared to traditional models for both living donor and deceased donor liver transplantation. This program was coded by chatGPT implementing the graft survival prediction model developed by the article. ABC model stands for AST, Bilirubin, Coagulation factor. You can put maximum AST level during 0-7 days post-LT, maximum Total bilirubin level during 3-7 days, maximum INR level during 3-7 days. The day after LT is for calculating the probability of survival after LT. It shows you the exact number as well as the survival curve. Use it freely and when writing a paper, please make a citation on the article.
Author jsrrules@gmail.com
Date 2025.02.03
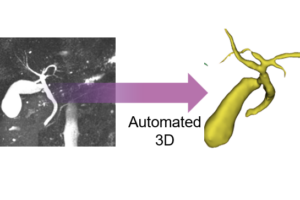
3D auto-segmentation of biliary structure of living liver donors using magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography for enhanced
Background: This study aimed to develop an automated segmentation system for biliary structures using a deep learning model, based on data from magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Materials and methods: Living liver donors who underwent MRCP using the gradient and spin echo technique followed by three-dimensional modeling were eligible for this study. A three-dimensional residual U-Net model was implemented for the deep learning process. Data were divided into training and test sets at a 9:1 ratio. Performance was assessed using the dice similarity coefficient to compare the model’s segmentation with the manually labeled ground truth. Results: The study incorporated 250 cases. There was no difference in the baseline characteristics between the train set (n =225) and test set (n=25). The overall mean Dice Similarity Coefficient was 0.80 ± 0.20 between the ground truth and inference result. The qualitative assessment of the model showed relatively high accuracy especially for the common bile duct (88%), common hepatic duct (92%), hilum (96%), right hepatic duct (100%), and left hepatic duct (96%), while the third-order branch of the right hepatic duct (18.2%) showed low accuracy. Conclusion: The developed automated segmentation model for biliary structures, utilizing MRCP data and deep learning techniques, demonstrated robust performance and holds potential for further advancements in automation 배경: 본 연구는 자기공명 담췌관조영술(MRCP) 데이터를 기반으로 심층 학습 모델을 활용하여 담도 구조를 자동으로 분할하는 시스템을 개발하는 것을 목표로 하였습니다. 재료 및 방법: Gradient 및 Spin Echo 기법을 사용하여 MRCP를 시행한 후 3D 모델링을 수행한 생체 간 기증자가 본 연구에 포함되었습니다. 심층 학습 과정에서는 3D 잔여 U-Net(Residual U-Net) 모델을 구현하였으며, 데이터를 9:1 비율로 학습 세트와 테스트 세트로 나누어 분석하였습니다. 모델의 분할 성능은 수동으로 라벨링된 기준 데이터(ground truth)와 비교하여 Dice 유사도 계수를 사용해 평가하였습니다. 결과: 연구에는 총 250건의 사례가 포함되었으며, 학습 세트(n=225)와 테스트 세트(n=25) 간에 기초 특성의 차이는 없었습니다. 기준 데이터와 모델 추론 결과 간의 평균 Dice 유사도 계수는 0.80 ± 0.20이었습니다. 모델의 질적 평가는 비교적 높은 정확도를 보였으며, 특히 총담관(88%), 총간관(92%), 간문부(96%), 우간관(100%), 좌간관(96%)에서 높은 정확도를 나타냈습니다. 반면, 우간관 3차 분지(18.2%)에서는 낮은 정확도를 보였습니다. 결론: MRCP 데이터와 심층 학습 기술을 활용하여 개발된 담도 구조 자동 분할 모델은 강력한 성능을 입증하였으며, 자동화 기술의 발전 가능성을 보여주었습니다.
Author jsrrules
Date 2024.12.13
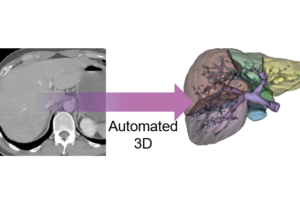
Comprehensive deep learning-based assessment of living liver donor CT angiography: from vascular segmentation to volumetric ana
Background: Precise preoperative assessment of liver vasculature and volume in living donor liver transplantation is essential for donor safety and recipient surgery. Traditional manual segmentation methods are being supplemented by deep learning (DL) models, which may offer more consistent and efficient volumetric evaluations. Methods: This study analyzed living liver donors from Samsung Medical Center using preoperative CT angiography data between April 2022 and February 2023. A DL-based 3D residual U-Net model was developed and trained on segmented CT images to calculate the liver volume and segment vasculature, with its performance compared to traditional manual segmentation by surgeons and actual graft weight. Results: The DL model achieved high concordance with manual methods, exhibiting Dice Similarity Coefficients of 0.94 ± 0.01 for the right lobe and 0.91 ± 0.02 for the left lobe. The liver volume estimates by DL model closely matched those of surgeons, with a mean discrepancy of 9.18 ml, and correlated more strongly with actual graft weights (R-squared value of 0.76 compared to 0.68 for surgeons). Conclusion: The DL model demonstrates potential as a reliable tool for enhancing preoperative planning in liver transplantation, offering consistency and efficiency in volumetric assessment. Further validation is required to establish its generalizability across various clinical settings and imaging protocols. 배경: 생체 간이식에서 기증자의 안전과 수혜자의 수술을 위해 간 혈관과 용적에 대한 정확한 수술 전 평가가 필수적입니다. 기존의 수작업 분할 방법은 심층 학습(Deep Learning, DL) 모델에 의해 보완되고 있으며, 이는 보다 일관되고 효율적인 용적 평가를 제공할 수 있습니다. 방법: 본 연구는 2022년 4월부터 2023년 2월까지 삼성서울병원에서 생체 간 기증자를 대상으로 한 수술 전 CT 혈관조영 데이터를 분석하였습니다. 3D 잔여 U-Net(Residual U-Net) 기반의 DL 모델을 개발하여 간의 용적과 혈관을 분할 및 계산하였으며, 해당 성능은 외과의가 수행한 기존 수작업 분할 및 실제 이식 간 중량과 비교되었습니다. 결과: DL 모델은 수작업 방법과 높은 일치도를 보였으며, 우엽의 Dice 유사도 계수(Dice Similarity Coefficient)는 0.94 ± 0.01, 좌엽은 0.91 ± 0.02로 나타났습니다. DL 모델이 추정한 간 용적은 외과의의 결과와 평균 9.18ml의 차이를 보였으며, 실제 이식 간 중량과 더 높은 상관관계(R²=0.76, 외과의 R²=0.68)를 나타냈습니다. 결론: DL 모델은 간이식 수술 전 계획을 향상시키는 신뢰할 수 있는 도구로서 잠재력을 보여주었으며, 용적 평가의 일관성과 효율성을 제공합니다. 다양한 임상 환경과 영상 프로토콜에서의 일반화 가능성을 입증하기 위해 추가적인 검증이 필요합니다.
Author jsrrules
Date 2024.12.13
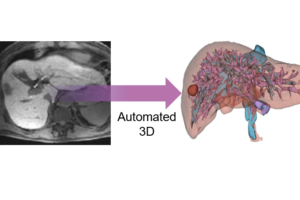
Automated 3D liver segmentation from hepatobiliary phase MRI for enhanced preoperative planning
Recent advancements in deep learning have facilitated significant progress in medical image analysis. However, there is lack of studies specifically addressing the needs of surgeons in terms of practicality and precision for surgical planning. Accurate understanding of anatomical structures, such as the liver and its intrahepatic structures, is crucial for preoperative planning from a surgeon’s standpoint. This study proposes a deep learning model for automatic segmentation of liver parenchyma, vascular and biliary structures, and tumor mass in hepatobiliary phase liver MRI to improve preoperative planning and enhance patient outcomes. A total of 120 adult patients who underwent liver resection due to hepatic mass and had preoperative gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI were included in the study. A 3D residual U-Net model was developed for automatic segmentation of liver parenchyma, tumor mass, hepatic vein (HV), portal vein (PV), and bile duct (BD). The model’s performance was assessed using Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) by comparing the results with manually delineated structures. The model achieved high accuracy in segmenting liver parenchyma (DSC 0.92 ± 0.03), tumor mass (DSC 0.77 ± 0.21), hepatic vein (DSC 0.70 ± 0.05), portal vein (DSC 0.61 ± 0.03), and bile duct (DSC 0.58 ± 0.15). The study demonstrated the potential of the 3D residual U-Net model to provide a comprehensive understanding of liver anatomy and tumors for preoperative planning, potentially leading to improved surgical outcomes and increased patient safety. 심층 학습의 최근 발전은 의료 영상 분석에서 상당한 진전을 가능하게 했습니다. 그러나 수술 계획의 실용성과 정확성 측면에서 외과의의 요구를 구체적으로 다룬 연구는 부족한 실정입니다. 외과의의 관점에서 간 및 간내 구조와 같은 해부학적 구조를 정확히 이해하는 것은 수술 전 계획에 매우 중요합니다. 본 연구는 간담췌 단계 간 MRI에서 간 실질, 혈관 및 담도 구조, 종양 덩어리를 자동으로 분할하기 위한 심층 학습 모델을 제안하여 수술 전 계획을 개선하고 환자 결과를 향상시키는 것을 목표로 합니다. 총 120명의 성인을 대상으로 연구를 진행했으며, 이들은 간 종양으로 인해 간 절제술을 받았고, 수술 전 가독세트산 강화 MRI를 시행하였습니다. 간 실질, 종양, 간 정맥(HV), 문맥(PV), 담도(BD)를 자동으로 분할하기 위해 3D 잔여 U-Net(Residual U-Net) 모델을 개발하였고, 수작업으로 표시된 구조와 비교하여 Dice 유사도 계수(DSC)를 사용해 모델의 성능을 평가하였습니다. 모델은 간 실질(DSC 0.92 ± 0.03), 종양 (DSC 0.77 ± 0.21), 간 정맥(DSC 0.70 ± 0.05), 문맥(DSC 0.61 ± 0.03), 담도(DSC 0.58 ± 0.15)의 분할에서 높은 정확도를 달성했습니다. 본 연구는 3D 잔여 U-Net 모델이 간 해부학 및 종양에 대한 포괄적인 이해를 제공하여 수술 전 계획을 개선하고, 궁극적으로 수술 결과를 향상시키며 환자 안전성을 높이는 데 기여할 가능성을 입증하였습니다.